| [1]Fairless R, Barnett SC. Olfactory ensheathing cells: their role in central nervous system repair. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005; 37(4):693-699.
[2]Ramer LM, Au E, Richter MW, et al. Peripheral olfactory ensheathing cells reduce scar and cavity formation and promote regeneration after spinal cord injury. J Comp Neurol. 2004;473(1):1-15.
[3]Lee JY, Kim KH, Shin SY, et al. Enhanced bone formation by transforming growth factor- beta1- releasing collagen/ chitosan microgranules. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2006; 76(3): 530- 539.
[4]Zhang Y, Cheng X, Wang J, et al. Novel chitosan/collagen scaffold containing transforming growth factor-beta1 DNA for periodontal tissue engineering. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;344(1):362-369.
[5]The Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China. Guidance suggestion of caring laboratory animals. 2006-09-30.
[6]常瑞,阴小龙.预损伤嗅粘膜对自体嗅鞘细胞体外培养的作用[J].中国组织工程与临床康复,2008,12(51):10001-10004.
[7]廖文,刘淑红,张世强,等.壳聚糖导管复合自体骨髓间充质干细胞修复大鼠13 mm坐骨神经缺损[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2007,11(18):3517-3522.
[8]Keilhoff G, Goihl A, Stang F, et al. Peripheral nerve tissue engineering: autologous Schwann cells vs transdifferentiated mesenchymal stem cells. Tissue Eng. 2006;12(6):1451-1465.
[9]梁楠,张晓,徐艳.神经组织工程细胞外基质材料研究进展[J].西南军医,2006, 8(6):69-72.
[10]Leffler CC, Muller BW. Influence of the acid type on the physical and drug liberation properties of chitosan-gelatin sponges. Int J Pharm. 2000;194(2):229-237.
[11]Chandy T, Sharma CP. Chitosan-as a biomaterial. Biomat Art Cells Art Org. 1999;18(1):1-24.
[12]Takeda Y, Asou H, Murakami Y, et al. A nonneuronal isoform of cell adhesion molecule L1: tissue-specific expression and functional analysis. J Neurochem. 1996;66(6):2338-2349.
[13]Schnell L, Fearn S, Klassen H, et al. Acute inflammatory responses to mechanical lesions in the CNS: differences between brain and spinal cord. Eur J Neurosci. 1999;11(10): 3648-3658.
[14]Kakulas BA. A review of the neuropathology of human spinal cord injury with emphasis on special features. J Spinal Cord Med. 1999;22(2):119-124.
[15]McPhail LT, Stirling DP, Tetzlaff W, et al. The contribution of activated phagocytes and myelin degeneration to axonal retraction/dieback following spinal cord injury. Eur J Neurosci. 2004;20(8):1984-1994.
[16]Murthy M, Bocking S, Verginelli F, et al. Transcription factor Runx1 inhibits proliferation and promotes developmental maturation in a selected population of inner olfactory nerve layer olfactory ensheathing cells. Gene. 2014;540(2): 191-200.
[17]Botero L, Gomez RM, Chaparro O. Pathogenesis of spinal cord injuries and mechanisms of repair induced by olfactory ensheathing cells. Rev Neurol. 2013;56(10):521-531.
[18]Qi F, Wang Y, Ma T, et al. Electrical regulation of olfactory ensheathing cells using conductive polypyrrole/chitosan polymers. Biomaterials. 2013;34(7):1799-809.
[19]Campisi A, Spatuzza M, Russo A, et al. Expression of tissue transglutaminase on primary olfactory ensheathing cells cultures exposed to stress conditions. Neurosci Res. 2012; 72(4): 289-295.
[20]Tharion G, Indirani K, Durai M, et al. Motor recovery following olfactory ensheathing cell transplantation in rats with spinal cord injury. Neurol India. 2011;59(4):566-572.
[21]Simón D, Martín-Bermejo MJ, Gallego-Hernández MT, et al. Expression of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 by olfactory ensheathing glia promotes axonal regeneration. Glia. 2011; 59(10):1458-1471.
[22]Lu ZF, Shen YX, Zhang P, et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 promotes proliferation and neurotrophin expression of olfactory ensheathing cells. J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2010;12(4): 265-272.
[23]Yan HB, Zhang ZM, Jin DD, et al. The repair of acute spinal cord injury in rats by olfactory ensheathing cells graft modified by glia cell line-derived neurotrophic factor gene in combination with the injection of monoclonal antibody IN-1. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2009;47(23):1817-1820.
[24]Scott AL, Ramer MS. Schwann cell p75NTR prevents spontaneous sensory reinnervation of the adult spinal cord. Brain. 2010;133(Pt 2):421-432.
[25]Pellitteri R, Spatuzza M, Stanzani S, et al. Biomarkers expression in rat olfactory ensheathing cells. Front Biosci (Schol Ed). 2010;2:289-298.
[26]Radtke C, Schmitz B, Spies M, et al. Peripheral glial cell differentiation from neurospheres derived from adipose mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2009;27(8): 817-823.
[27]Kocsis JD, Lankford KL, Sasaki M, et al. Unique in vivo properties of olfactory ensheathing cells that may contribute to neural repair and protection following spinal cord injury. Neurosci Lett. 2009;456(3):137-142.
[28]Runyan SA, Phelps PE. Mouse olfactory ensheathing glia enhance axon outgrowth on a myelin substrate in vitro. Exp Neurol. 2009;216(1):95-104.
[29]Bretzner F, Liu J, Currie E, et al. Undesired effects of a combinatorial treatment for spinal cord injury--transplantation of olfactory ensheathing cells and BDNF infusion to the red nucleus. Eur J Neurosci. 2008;28(9):1795-807.
[30]Shyu WC, Liu DD, Lin SZ, et al. Implantation of olfactory ensheathing cells promotes neuroplasticity in murine models of stroke. J Clin Invest. 2008;118(7):2482-2495.
[31]Guest JD, Herrera L, Margitich I, et al. Xenografts of expanded primate olfactory ensheathing glia support transient behavioral recovery that is independent of serotonergic or corticospinal axonal regeneration in nude rats following spinal cord transection. Exp Neurol. 2008;212(2):261-274.
[32]Wu J, Sun TS, Ren JX, et al. Ex vivo non-viral vector-mediated neurotrophin-3 gene transfer to olfactory ensheathing glia: effects on axonal regeneration and functional recovery after implantation in rats with spinal cord injury. Neurosci Bull. 2008;24(2):57-65.
[33]Furukawa S, Furukawa Y. FGF-2-treatment improves locomotor function via axonal regeneration in the transected rat spinal cord. Brain Nerve. 2007;59(12):1333-1339.
[34]Pellitteri R, Spatuzza M, Russo A, et al. Olfactory ensheathing cells exert a trophic effect on the hypothalamic neurons in vitro. Neurosci Lett. 2007;417(1):24-29.
[35]Raisman G, Li Y. Repair of neural pathways by olfactory ensheathing cells. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007;8(4):312-319.
[36]Pastrana E, Moreno-Flores MT, Avila J, et al. BDNF production by olfactory ensheathing cells contributes to axonal regeneration of cultured adult CNS neurons. Neurochem Int. 2007;50(3):491-498.
[37]Cao L, Su Z, Zhou Q, et al. Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor promotes olfactory ensheathing cells migration. Glia. 2006;54(6):536-544.
[38]Cui Q. Actions of neurotrophic factors and their signaling pathways in neuronal survival and axonal regeneration. Mol Neurobiol. 2006;33(2):155-179.
[39]Marshall CT, Lu C, Winstead W, et al. The therapeutic potential of human olfactory-derived stem cells. Histol Histopathol. 2006;21(6):633-643.
[40]Steward O, Sharp K, Selvan G, et al. A re-assessment of the consequences of delayed transplantation of olfactory lamina propria following complete spinal cord transection in rats. Exp Neurol. 2006;198(2):483-499.
[41]Kumar R, Hayat S, Felts P, et al. Functional differences and interactions between phenotypic subpopulations of olfactory ensheathing cells in promoting CNS axonal regeneration. Glia. 2005;50(1):12-20.
[42]Wewetzer K, Kern N, Ebel C, Radtke C, Brandes G. Phagocytosis of O4+ axonal fragments in vitro by p75- neonatal rat olfactory ensheathing cells. Glia. 2005;49(4): 577-587.
[43]Williams SK, Franklin RJ, Barnett SC. Response of olfactory ensheathing cells to the degeneration and regeneration of the peripheral olfactory system and the involvement of the neuregulins. J Comp Neurol. 2004;470(1):50-62.
[44]Hendriks WT, Ruitenberg MJ, Blits B, et al. Viral vector-mediated gene transfer of neurotrophins to promote regeneration of the injured spinal cord. Prog Brain Res. 2004; 146:451-476.
[45]Woodhall E, West AK, Vickers JC, et al. Olfactory ensheathing cell phenotype following implantation in the lesioned spinal cord. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2003;60(10): 2241-2253.
[46]Biers SM, Brading AF. Nerve regeneration: might this be the only solution for functional problems of the urinary tract? Curr Opin Urol. 2003;13(6):495-500.
[47]Ruitenberg MJ, Plant GW, Hamers FP, et al. Ex vivo adenoviral vector-mediated neurotrophin gene transfer to olfactory ensheathing glia: effects on rubrospinal tract regeneration, lesion size, and functional recovery after implantation in the injured rat spinal cord. J Neurosci. 2003; 23(18):7045-7058.
[48]Lipson AC, Widenfalk J, Lindqvist E, et al. Neurotrophic properties of olfactory ensheathing glia. Exp Neurol. 2003; 180(2):167-171.
[49]Shen H, Tang Y, Wu Y, et al. Influences of olfactory ensheathing cells transplantation on axonal regeneration in spinal cord of adult rats. Chin J Traumatol. 2002;5(3): 136-141.
[50]Kwon BK, Tetzlaff W. Spinal cord regeneration: from gene to transplants. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(24 Suppl): S13-22.
[51]Lacroix S, Tuszynski MH. Neurotrophic factors and gene therapy in spinal cord injury. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2000;14(4):265-275.
[52]Nash HH, Borke RC, Anders JJ. New method of purification for establishing primary cultures of ensheathing cells from the adult olfactory bulb. Glia. 2001;34(2):81-87.
[53]Woodhall E, West AK, Chuah MI. Cultured olfactory ensheathing cells express nerve growth factor, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, glia cell line-derived neurotrophic factor and their receptors. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2001;88(1-2): 203-213.
[54]Fry EJ. Central nervous system regeneration: mission impossible? Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2001;28(4): 253-258.
[55]Boruch AV, Conners JJ, Pipitone M, et al. Neurotrophic and migratory properties of an olfactory ensheathing cell line. Glia. 2001;33(3):225-229.
[56]Ramón-Cueto A, Nieto-Sampedro M. Regeneration into the spinal cord of transected dorsal root axons is promoted by ensheathing glia transplants. Exp Neurol. 1994;127(2): 232-244.
[57]Ramón-Cueto A, Pérez J, Nieto-Sampedro M. In vitro enfolding of olfactory neurites by p75 NGF receptor positive ensheathing cells from adult rat olfactory bulb. Eur J Neurosci. 1993;5(9):1172-1180. |
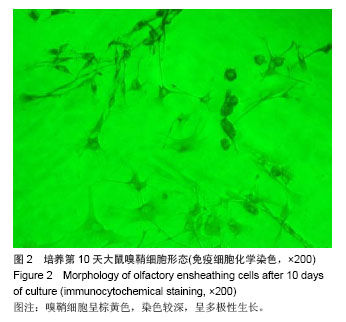
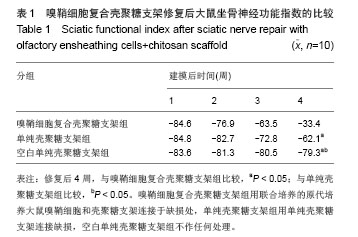
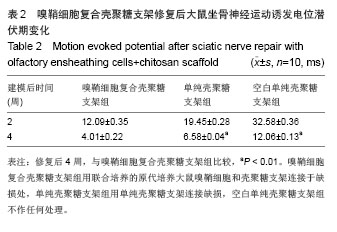
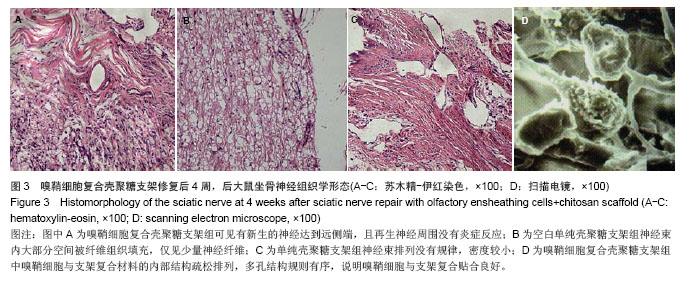
.jpg)
.jpg)